Optimize your internet speed by understanding data transfer rates, measured in megabits per second (Mbps) and gigabits per second (Gbps). Mbps represents 1,000,000 bits per second, while Gbps denotes 1,000,000,000 bits per second. Higher Mbps or Gbps indicates faster internet. Your chosen speed should align with your internet requirements. While Mbps is more prevalent for typical usage, Gbps suits households with heavy data demands, such as gamers and remote workers.
What is internet speed and why does it matter?
Internet speed refers to how much data and information can be transferred over the web on a single connection at any given time.
This is important for consumers to understand internet speed because it determines what types of activities you can do on the internet and how many devices you can connect to at once. Understanding how you and your family use the internet at home will help you determine which internet speeds you need to get from your provider.
If your internet speed is too slow, you might run into trouble performing tasks on the web like streaming video, playing video games or uploading files. If it’s too fast, you could be overpaying for internet services.
What can affect your internet speed?
Many elements can affect what speed you get. Here are a few things to consider:
- The type of internet connection you have, LTE or fiber
- The number of people using the same network at the same time
- The type of device you’re using
- The quality of the internet connection in your area
- The type of website or online service you’re using, such as streaming video or playing online games.
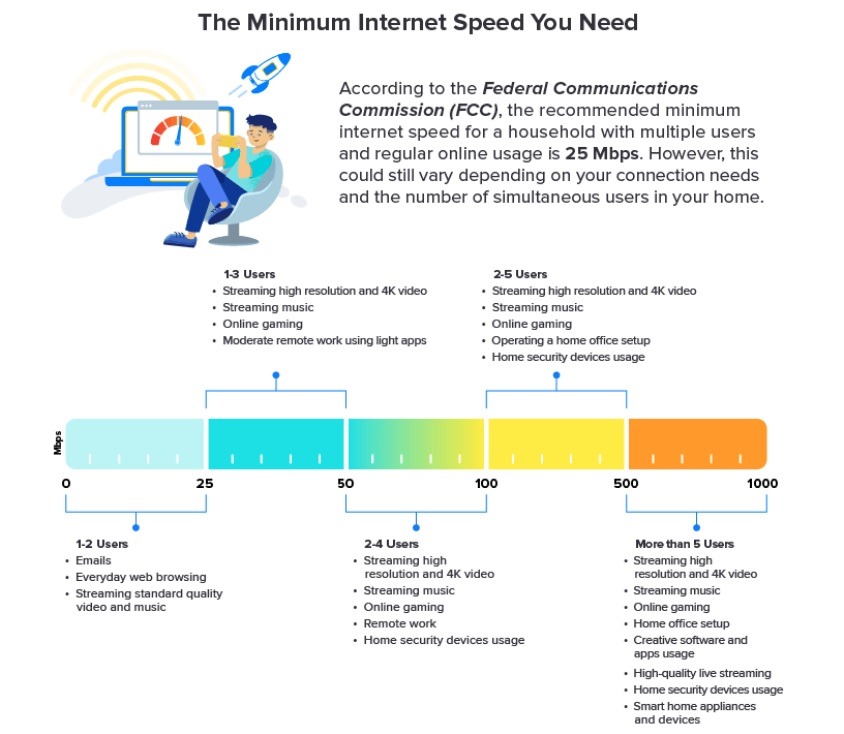
Understanding internet speeds by activity
Your internet speed needs really depend on your usage. Keep in mind that these are the speeds required for each device in your home. If you have multiple devices online at a time, you will need a faster plan.
For gamers, at a minimum, you need 4–8 Mbps for online gaming. For consistently efficient gaming, 10–25 Mbps tend to be best. Working from home, you will want a plan of at least 60 to 100 Mbps. If you frequently download and upload large files, you’ll want internet speeds of at least 50 Mbps. For simpler computer programs (word processing, for example), you can get by with just 3–4 Mbps.
For lots of video conferencing, you’ll want to sit somewhere in the middle with at least 10 Mbps. To stream videos, you’ll need at least 3 Mbps. It takes at least 25 Mbps for 4K streaming on your computer or Ultra HD-enabled devices.
Malware
Malware can infect your computer’s hardware, software or applications. One type is internet malware that infects computer applications such as web browsers. This kind of malware can open multiple browsers in the background, which can slow internet speeds.
Few ways to speed up your Wi-Fi:
- Make it a habit to restart your router. This allows them to “refresh” and clear stored up data.
- Switch from your 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi channel to the 5 GHz one. A 5 GHz channel has 23 overlapping channels compared to 16 for 2.4 GHz, which can increase speeds.
- Angle one Wi-Fi antenna straight up and the other to the side. This will send the connection both directly up and down through ceilings and horizontally through walls for well-rounded coverage.